Rare earth oxides (REO), titanium and nickel have become crucial in our every day lives. We can find nickel in stainless steel and lithium-ion batteries, the latter of which is ever more desirable in an environmentally conscious society. So how do you navigate such a rapidly evolving market? Michael Dempster, Professor Emeritus at the Centre For Financial Research, Department Of Pure Mathematics And Statistics, University Of Cambridge, shares how he models high-tech metal collateral, designs 100% risk free securities with third party derivatives, and implements security pricing and trading methodology.
Exotic high-tech metals such as rare earth oxides, titanium and nickel wire are increasingly important to semi-conductor, aerospace and high-end defence technology R & D and production. As a result – while not market traded and therefore sporadic order dependent and highly volatile – prices of these commodities have been rising on average over the past decade.
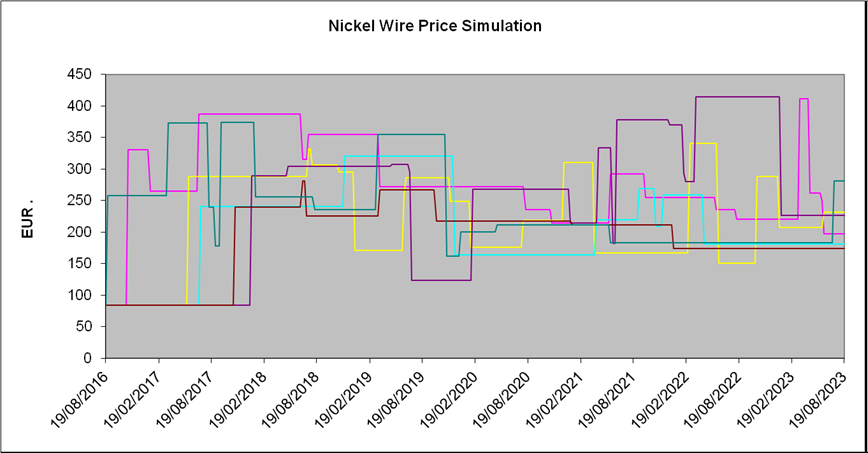
The metals trading subsidiary of an international group acquired over 6 million metres of nickel wire which is 99.9% pure nickel, thinner than a human hair and worth at the current market price of about 300 EUR per metre over 1.6 billion EUR. The firm wished to raise from 300 million to 1 billion EUR in the capital markets in order to purchase a variety of these high-tech metals to take advantage over the medium term (5 to 10 years) of generally rising prices.
My talk at QuantMinds International will discuss the technical pricing and default risk analysis for an example 350 million EUR 7 year amortised corporate bond issue backed by a nickel wire inventory and subsequent high-tech metal trading as collateral. Topics covered include security modelling with high-tech metal collateral, the design of 100% risk free securities with third party derivatives and security pricing and trading methodology.
The first risk free issue solution involved covering bond payments by sales from the nickel wire inventory and the purchase of put options from an AA rated derivative dealer by the issuer. However, the put option premia represented far too large a proportion of the issue. So the issuer and the dealer agreed to share the proceeds of collateral sales by means of the dealer purchasing call options on the sale proceeds from the issuer to make the net premia for 100% bond holder security acceptable to the issuer.
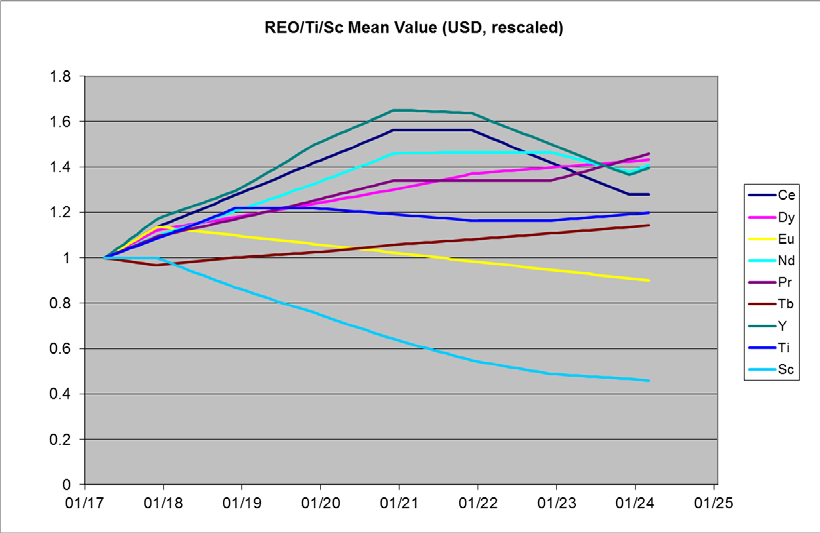
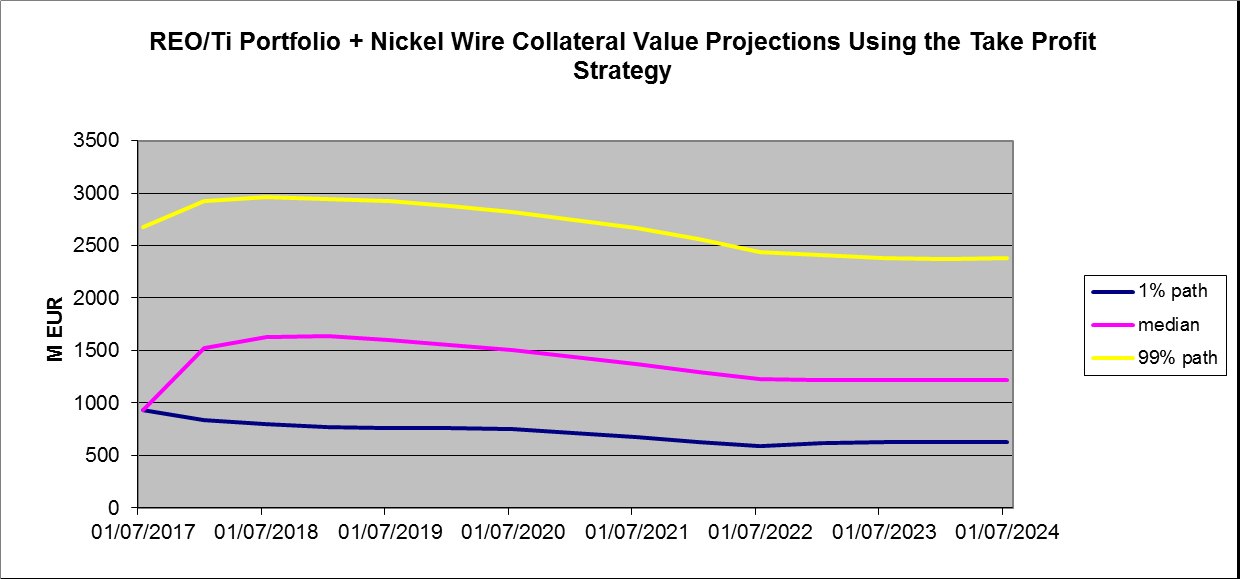
This solution was refined by the broker-dealer for the bond issue to require the issuer to profitably trade a portfolio of high-tech metals purchased initially from the issue receipts, as well as selling nickel wire collateral as necessary to cover the semi-annual bond payments as before. This required both forward price forecasts for titanium and a number of rare earth oxides (Ti/REO) and a semi-annual trading strategy for these portfolio elements at reset dates. A number of alternative trading strategies were evaluated with the surprising result that trading profits to cover bond payments were relatively insensitive to which of these strategies were employed, although selling the portfolio element with the highest historical return at the sale date was marginally optimal.
In more detail, the 7 year bond pays a basic semi-annual senior coupon of 6% after a two year grace period and is amortised with an annual amortisation schedule of 10% capital repayment in year 3, 15% in year 4, 20% in year 5, 25% in year 6 and 30% in year 7 with an option to redeem the bond in part or in full on each coupon date for the issuer. The day count is 30/360. A junior coupon payment of 3.626% is made semi-annually from year 3 to give an internal rate of return of 12%.
The complex stochastic analysis and Monte Carlo simulation analysis presented is based in part on specially developed modelling of the nickel wire catalogue price and third party price projections for rare earth oxides and titanium for which the market is more liquid than that for nickel wire. The analysis supports an optimistic view in that after accounting for all ongoing costs we again find a zero default probability for the bond issue – a situation seldom seen to accompany its stipulated 12% internal rate of return.
The reported research was carried out with the collaboration of M H A Davis (Imperial College) and G W P Thompson (CSA).

